In the past decade, flexographic printing has developed rapidly and is increasingly becoming the first choice for environmentally friendly green printing processes at home and abroad. The core power of the rapid development of flexographic printing is not only the continuous improvement of flexographic technology and equipment, but also the widespread use of printed materials that meet the requirements of green environmental protection, and in particular the widespread use of aqueous printing inks and UV printing inks. At present, most of the domestic water-based inks are not resistant to water, dry slowly, poor gloss, easy to cause paper shrinkage and other ills. In order to overcome the above drawbacks, some use flexographic UV inks, and some use imported high-grade water-based inks, which increases the printing cost. All these have caused China's flexographic printing to be restricted, which has restricted the development of China's packaging and printing industry. Therefore, it is very necessary to discuss the key “components†that determine the performance of water-based inks, the linking materials.
First, the theoretical part
Acrylic resin has two forms in the water-based ink binder: one is the alkali-soluble resin of acrylic acid that forms a resin solution by amination, commonly known as resin oil. It is the main body of the linking material. It uses Song to disperse the pigment and prepare base ink. The properties and solids content of the resin itself directly affect the viscosity of the water-based ink, the pigment dispersion properties, and the ink transfer properties. The other is an emulsion, which is formed by emulsion polymerization of acrylic acid, methacrylic acid, or other monomers (such as styrene), also has a certain degree of polymerization and acidity, and these properties directly depend on the control of conditions in the emulsion polymerization. . It is also because the conditions of emulsion polymerization are harsh and difficult to control, and the performance of the emulsion becomes even more important. The application of the emulsion in the water-based ink has a significant effect on improving the gloss, water resistance, and drying of the ink. Emulsions can be classified into film-forming emulsions or non-film-forming emulsions depending on their properties. According to different substrates, the proportion of these two emulsions in water-based inks is also different.
Emulsion generally refers to a polymer (a variety of lipids) that is dispersed as an emulsion in an aqueous medium with the aid of an emulsifier under mechanical stirring or vigorous shaking. The polymer is also used in polymerization. Initiators and pH regulators and other additives. The reason why emulsions become emulsions is the emulsifier. Emulsifier is actually a kind of surfactant, its function is to reduce the surface tension of monomer and water, so that monomer and water form a stable and uniform system. Micelles and emulsified monomer droplets are formed, often using anionic and non-ionic surfactants. Because of this special composition of the emulsion, adding it to the water-based ink, on the one hand, acts as a resin binder, and on the other hand, it also functions as a surfactant. When the emulsion is added, it can infiltrate the pigment faster than ordinary binders and penetrate into the pores of the pigment particle aggregates, which is the main part of pigment dispersion. Adding the emulsion can reduce the surface tension of the system, and when the surface tension decreases, the ink will have better wetting, adhesion, and soaking effects on the surface of the substrate. The leveling performance will be improved, and the film surface will be smoother. Therefore, the glossiness is improved, and when the dispersion of the pigment is stabilized, the stability of the ink system is actually improved, and the water resistance and the friction resistance are also improved along with the improvement of the dispersion stability.
Tg (glass transition temperature) is one of the important indicators for selecting an emulsion polymer. As shown in FIG. 1 , the state of the polymer at different temperatures is different, ie, the emulsion polypolymers with different Tg have different film forming properties.
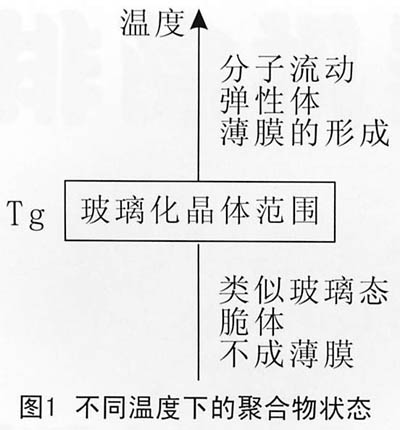
Film formation depends on mutual dissolution and interpenetration of polymer latex particles. If the polymer is too hard and the MFT is high, close to or higher than the application temperature, the latex particles cannot form a complete film or the film formation is insufficient, water resistance, durability may decrease, the coating film may have a poor luster, and micro cracks or hair may occur. Non-uniformity of color: If the emulsion polymer is too soft, the mechanical properties of the coating film are reduced, easy scratching, and the stain resistance is reduced. In addition, it takes time for the latex particles to infiltrate each other and dissolve each other, so the moisture should not be evaporated too quickly. The slower the evaporation of water, the better the dissolution of latex particles and the higher the film formation quality. However, in order to meet the requirements of high speed, quick drying, and other properties such as high printability and fastness of printing properties, heating, plasticizers, aggregating agents, and polymer blending methods can be used. The method is a mixture of polymers - that is, the addition of a soft polymer in a hard and brittle film system can promote the formation of thin films, and the use of soft polymers does not increase the organic volatiles.
This function of the emulsion can be analyzed using the following instructions:
Three forces are in equilibrium when the droplet is in contact with a solid surface, see Figure 2.

In the picture: θS is the solid surface tension, which is the force of the liquid spreading on the solid surface and has the function of expanding the solid and gas interface area:
θL is the surface tension of the liquid:
θSL is a force that promotes the reduction of the interface area between the solid and the liquid. It is called the interfacial tension between a liquid and a solid. α is the contact angle.
When the three forces reach equilibrium,
COSα=(θS-θSL)/θL
When α approaches 0°, the COS α approaches 1, and the wettability of the liquid to the solid reaches its maximum value. In this case, intimate contact is achieved. In order to increase the speed of wetting and spreading, a method of increasing θS or decreasing θL and θSL is generally adopted.
For the dispersion process of the ink, the surface energy of the pigment aggregate is θS, the surface energy after wetting by the binder is θS−(θSL+θL), and θS is fixed, so sufficient and rapid wetting is required. It is to reduce the surface tension (θL) of the binder and the interfacial tension (θSL) of the pigment/binder. Therefore, when the emulsion is further added to the ink system, its good surface activity capability allows both θL and θSL to decrease simultaneously, and the dispersion of the entire system is faster and more stable. (to be continued)
Candle pigments, also known as crayon pigments or candle dyes, are special pigments used to color candles. They are usually non-water-soluble and designed for candle making. They can be applied directly to the surface of the candle after the candle cools down, or mixed into the wax when the candle is melted to create a variety of colors and patterns. Common candle pigments are edible grade and industrial grade. Edible grade pigments are suitable for food-grade candles, such as birthday candles, while industrial grade pigments are suitable for artistic candles or decorative candles.
candle color dye,colour dye for candle making,candle material manufacture
China Senbo Industry Co.,ltd , https://www.yylpaper.com