Many engineers have such a habit: when measuring high-voltage signals, it is customary to disconnect the protection ground of the power plug, and use ordinary passive probes to directly perform high-pressure floating measurement. The result is "ah, I am electric!" ". Yes, you are not "electricized" by the beauty, you are really "electric", why in the end why this kind of electric shock? For the floating measurement, how much do you know?
Floating measurement
By disconnecting the protection ground of the oscilloscope's power plug (can be powered by a two-core power strip) or by using an isolating transformer to power the oscilloscope, the purpose of disconnecting the measurement loop is achieved, and the "floating" measurement is achieved, as shown in Figure 1. Shown.

Figure 1 oscilloscope power plug ground wire disconnected
The protective ground wire of the power plug can avoid the occurrence of electric leakage accidents or prevent the danger of strong electric power to the human body. If there is only the hot wire and the neutral wire, when the operator touches the high voltage power, the strong current will not be able to pass the current through the ground wire. Passing to the ground, but directly through the human body to the ground, resulting in an electric shock.

Figure 2 Human body electric shock
So what is the effect of disconnecting the protective ground of the power plug? See below.
1, 110V electric shock
Y capacitor is the capacitor connecting the live and ground of the power supply, the neutral and ground, as shown in Figure 3. It mainly acts as a filter protection and suppresses common mode interference. It belongs to the safety capacitor. After the capacitor fails. Will not cause electric shock, and will not cripple personal safety.
The metal housing of the oscilloscope (internal shield and exposed BNC head) is connected to the protective ground of the power plug. When the power plug is protected, the 220V voltage is divided by the Y capacitor, and the 110V voltage is directly applied to the oscilloscope. On the metal casing, that is, there is a 110V AC voltage on the metal casing. When a person touches the charged area, the pin-on electric shock phenomenon occurs. Although it does not crise personal safety, it is also a dangerous operation.
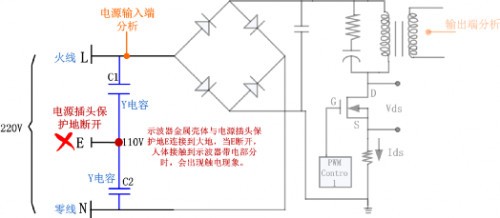
Figure 3 Y capacitor divider circuit
3, human body shock hazard
It can be seen from Figure 4 that after disconnecting the protection ground of the oscilloscope plug, the ordinary passive probe is directly connected to the high voltage module to be tested, that is, the oscilloscope metal case (the inner shield case and the exposed BNC head), and the probe ground. The terminal and the negative terminal of the high voltage module to be tested are at the same level, and are relatively large floating, and have a certain high voltage V (floating voltage V as shown in FIG. 4).
When the human body directly touches the conductive part of the oscilloscope, it is equivalent to directly contacting the high-voltage module under test, causing high-voltage current to flow directly into the earth through the human body, which may cause serious personal injury or even death! Therefore, "floating" measurement is very dangerous. , such operations may not be performed.
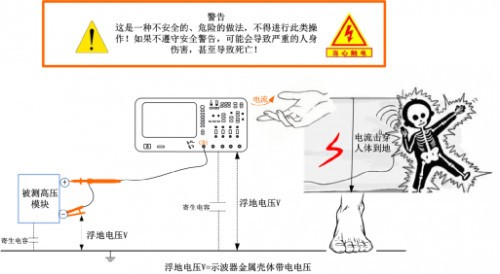
Figure 4 floating measurement of hazards
4, parameter measurement is not accurate
As shown in Figure 4, when floating measurements are taken, large parasitic capacitance and parasitic inductance are generated between the oscilloscope power supply and the ground. At higher frequencies, disconnecting the protective ground of the power line may not break the ground loop, so in addition to measuring the loop signal between the two ends of the probe, the signal of the "virtual" ground loop is added. The resulting ringing will distort the signal, resulting in inaccurate measurement data, as shown in Figure 5.
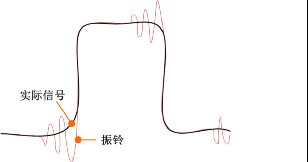
Figure 5 ringing phenomenon
5, the oscilloscope and the circuit under test is damaged
High voltage condition: Due to the high floating voltage between the oscilloscope and the real ground, the charge will accumulate on the oscillating device of the oscilloscope. This is an invisible hazard that will cause the oscilloscope to malfunction in future use. Since the ground of the probe is connected to the ground inside the oscilloscope, that is, to the outer casing, when the oscilloscope casing has a large amount of electric charge, it will cause the probe to burn out, eventually causing a series of accidents.
High parasitic capacitance: Due to the high parasitic capacitance, the device under test may have a small spark, which may damage the circuit under test.
Through the above introduction, floating measurement is a high-voltage measurement method that is neither safe nor accurate. It is recommended to use a high-voltage differential probe for safe and effective high-voltage measurement. The ZP1000D high-voltage differential probe can measure high-voltage power with a peak value of 1300V, that is, high-voltage band isolation, which can measure differential signals, high-voltage signals and high-voltage differential signals.

Dinnerware Sets,Dish Sets,Dinner Plate Sets,Black Dinner Set
Guangzhou Concept Home Ltd , https://www.concepthomelimited.com