introduction
The rapid development of modern science and technology, especially network and information, has made the Internet move toward broadband and high-speed. The pace of global informationization is getting faster and faster, and human beings have entered a networked life era. The development of information technology, computers, control technology and automation technology has made it possible to fully automate people's work and life, and created the indispensable conditions for their realization. With the rapid spread of computers and the Internet in the home, the advancement of smart devices, and the rapid development of radio technologies, the dream of remote control of home appliances has gradually become a reality. This paper carefully studies the security performance of smart cards and the transmission characteristics of U and WB. On this basis, a feasible network structure for remote management and control of home appliances is given. It is specifically proposed to embed a smart card system into a home gateway to further enhance the security performance of the smart home network.
1 smart card
A smart card is a card made by embedding an integrated circuit chip with storage, encryption, and data processing capabilities on a plastic substrate. The hardware is mainly composed of a microprocessor and a memory. Together with the smart card operating system (COS) and application software that is solidified in the card, a smart card constitutes a loss-proof and portable microcomputer. The hardware components of the smart card include: CPU, memory (including RAM, ROM and EEPROM, etc.), I/O interface for card and read/write terminal communication, and test and security logic, as shown in Figure 1.
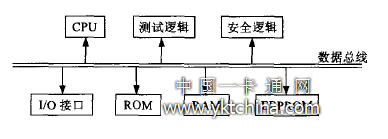
Figure 1 Hardware structure of the smart card
The microprocessor, which is the core of the chip, uses an 8-bit word-length CPU (the higher-end CPU is also starting to be applied) and is responsible for all operations and data exchange functions. The memory capacity of the card is generally not very large. Among them, the operating system code and the self-test program are solidified in the ROM, and the capacity depends on the microprocessor used, which is typically 32 KB; the RAM is used to store temporary data or Intermediate data, such as short-term passwords, temporary variables, and stack data, usually have a capacity of no more than 1 KB: EEPROM stores various application information of smart cards, such as encrypted data and application files, and sometimes includes some COS codes, and the capacity is usually Between 2KB and 32KB, this part of the storage resources can be exploited by users. The main function of the smart card operating system COS is to control the exchange of information between the smart card and the outside world, manage the memory in the smart card and complete the processing of various commands inside the card. The card exchanges information with the terminal in the form of a command-response pair. The existence of CPU and COS enables smart cards to easily use PIN verification, encryption technology and authentication technology to enhance the security of smart cards. The non-reproducibility of smart card hardware ensures that the user's identity is not spoofed. The smart card is carried by a legitimate user. When logging in, the smart card must be inserted into a dedicated card reader to read the information to verify the identity of the user. The user cannot obtain the access right by PIN or smart card only, and fails to try to input the PIN several times. After (3 times) the smart card is locked. The basic feature of smart cards is to provide a secure environment for data and programs. It is this feature that enables smart card systems to be embedded into smart home gateways to take advantage of their unique security technologies to enhance the security of home networks.
2 Ultra-wideband (UWB) technology
Ultra-wide bandwidth (UWB) pulse radio technology is a wireless communication technology emerging in the world in recent years. In 2002, the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) promulgated the latest UWB spectrum plan and specified that as long as a signal has an absolute bandwidth greater than 0.5 GHz at 10 dB or a partial bandwidth greater than 20%, and meets FCC power spectral density limits. The signal is the ultra-wideband signal. The FCC also specifies that the UWB system's 7.5 GHz bandwidth frequency between 3.1 and 10.6 GHz in the unlicensed band is the frequency range used by UWB. UWB is different from traditional narrowband wireless transmission technology and different from spread spectrum broadband technology in 3G cellular communication. UWB technology has the following characteristics: 1 spectrum is wide and power consumption is low. Ultra-wideband does not need to generate a sinusoidal carrier signal, and can directly transmit a time-hopping pseudo-random code (PN code) and an information-bit controlled impulse pulse sequence, thereby having a wide spectrum and a low average power, which is advantageous for coexistence with other systems. , improve spectrum utilization; 2 good confidentiality. Since the UWB signal adopts time-hopping spread spectrum, its RF bandwidth can reach above 1 GHz, and the transmit power spectral density is extremely low. The signal is concealed in the environmental noise and other information numbers, and can not be distinguished and received by the traditional transceiver; The device structure is simple. The UWB transmitter directly uses a pulsed small excitation antenna, and does not require a power amplifier and a mixer. At the same time, the UWB receiver does not require intermediate frequency processing. Therefore, the UWB system structure is relatively simple to implement; 4 the transmission rate is high. UWB's enormous bandwidth brings great system capacity, which is the fastest access method for wireless networks today. It is especially suitable for short-distance (<10 m) communication technologies: 5 multi-path resolution. The carrierless state of the ultra-wideband signal waveform results in only a small amount of fading when the pulses overlap. 6 Low radiation. UWB radiation is extremely low, only a 41 dBrn/MHz. These features make UWB especially suitable for home wireless LANs. Compared with other short-range wireless LAN communication technologies (such as Bluetooth technology, HomeRF, etc.) that work in a relatively narrow spectrum (as shown in Table 1), the advantages of UWB technology are obvious: within 10m, UWB can Plays up to hundreds of Mb/s of transmission performance; IEEE802.11a or HomeRF will be better than UWB in transmission distance, but HomeRF rate is too low, IEEE802.11a is used in home networks is a bit overkill; so look at UWB As a substitute for Bluetooth technology, it may be more suitable, because the latter transmission rate is far less than the former, and the protocol of Bluetooth technology is also more complicated. Therefore, UWB is perfect for use in smart home systems.
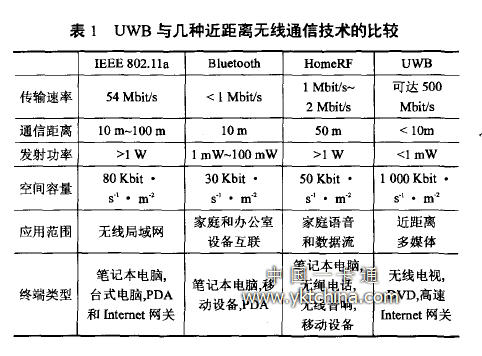
Comparison of UWB and several short-range wireless communication technologies
Our main product is : nylon cooking utensil , stainless steel kitchen utensil , kitchen grater. The stainless steel of our products can be in18/10 (AISI 316); 18/8 (AISI 304) and 18/0 (AISI 430)which are safe for touching food directly and we get SGS food safe test for our goods: LFGB for the whole European market ; FDA for North and South American market.We get our own design, meanwhile OEM is welcome, we can do not only the whole cutlery in stainless steel, but also can do colorful plastic handle; wooden handle . Your logo can be embossed; engraved; imprint and lasered. The finish of the cutlery we get mirror polish; matt polish; satin polish and also tumble polish(Machine polish).
Kitchen Tools,Knife Sharpener,Kitchen Utensils,Cooking Utensils,Vegetable Peeler,Wooden Grill Scraper,Vegetable Chopper
MEO DEMO CO., LTD. , https://www.meokitchenknives.com